Project leader: Professor Mark Febbraio
In a landmark 2019 Nature publication, we engineered a novel therapeutic called IC7Fc — a chimeric gp130 ligand that combines the beneficial properties of two naturally occurring proteins, IL-6 and CNTF. This innovative molecule addresses a critical challenge in metabolic disease treatment: how to improve metabolism without triggering inflammation or losing muscle mass.
A promising new approach
In preclinical studies, IC7Fc demonstrated remarkable efficacy across multiple metabolic parameters. The molecule improved glucose tolerance, reduced liver fat accumulation, prevented weight gain in obesity models and enhanced energy expenditure — all without the inflammatory side effects typically associated with cytokine-based therapies.
Crucially, IC7Fc showed an excellent safety profile not only in mice but also in non-human primates, with no signs of inflammation or immunogenicity. These promising results have paved the way for human clinical trials, which we're preparing to launch in partnership with Celesta Therapeutics using next-generation molecules based on IC7Fc.
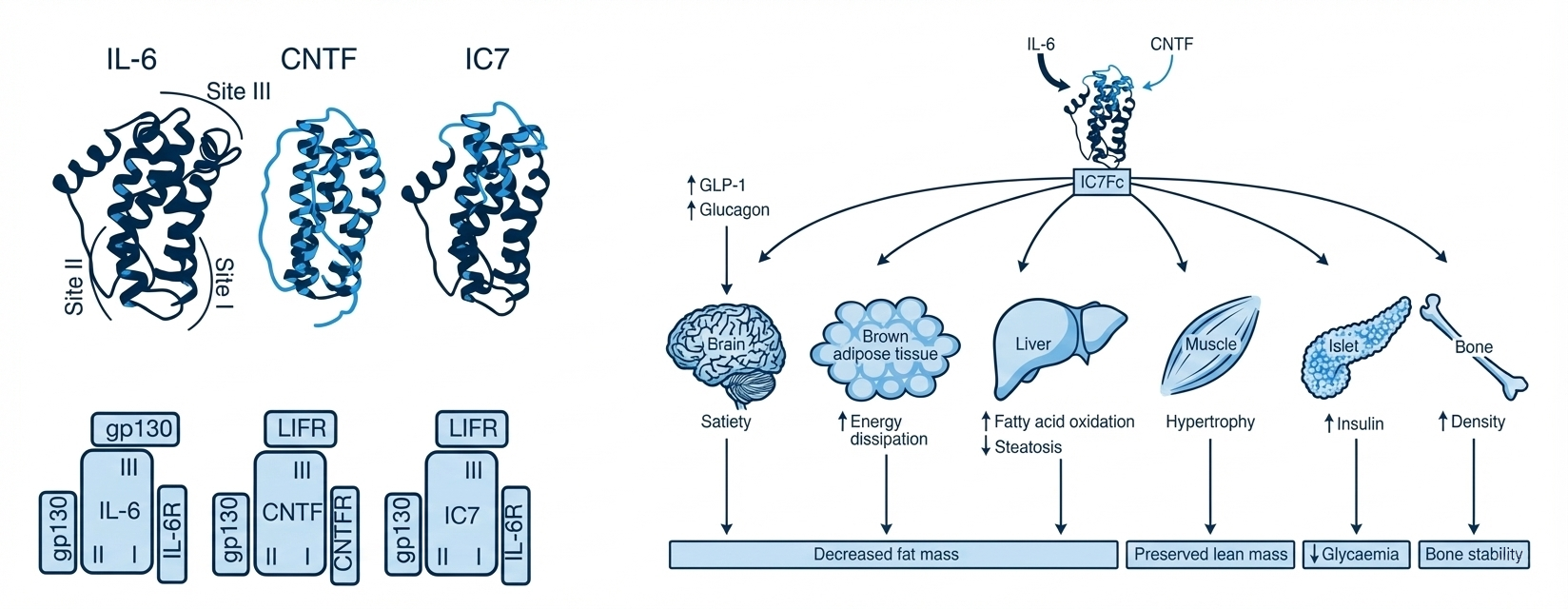
Figure: IC7Fc is a novel chimeric cytokine that protects against metabolic disease. The diagram shows how IC7Fc (a hybrid of IL-6 and CNTF) acts on multiple organs including the brain (satiety), brown adipose tissue (energy dissipation), liver (fatty acid oxidation, reduced steatosis), muscle (hypertrophy), fat (insulin sensitivity) and bone (density), leading to decreased fat mass whilst preserving lean mass and improving glycaemia and bone stability.
Addressing the muscle loss problem
One of IC7Fc's most intriguing properties is its ability to preserve muscle mass even when food intake is reduced. This discovery has important implications for current weight-loss treatments.
Glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) — drugs like semaglutide and tirzepatide — have revolutionised obesity and type 2 diabetes treatment with their remarkable efficacy for weight loss. However, they have a significant drawback: patients lose substantial muscle mass alongside fat. This muscle loss is often overlooked but represents a serious concern, particularly for older adults where muscle preservation is critical for maintaining independence and quality of life.
We hypothesise that IC7Fc could serve as an adjunct therapy to GLP-1RAs, enabling patients to achieve the weight loss benefits of these drugs while preserving muscle mass. This combination approach has emerged as a subject of intense interest in the pharmaceutical industry, as the market for GLP-1RAs expands rapidly and the muscle loss issue becomes increasingly apparent.
What makes IC7Fc unique
Unlike traditional cytokine therapies that can trigger widespread inflammation, IC7Fc has been engineered to selectively activate beneficial metabolic pathways whilst avoiding inflammatory responses. The molecule achieves this through its chimeric structure, which enables it to engage the gp130 receptor complex in a way that promotes metabolism without activating inflammatory signalling cascades.
By acting on multiple organs simultaneously — including the brain (reducing appetite), brown fat (increasing energy expenditure), liver (reducing fat accumulation), muscle (promoting growth), white fat (improving insulin sensitivity) and bone (increasing density) — IC7Fc addresses metabolic disease through multiple complementary mechanisms.
Next steps
Our ongoing work focuses on:
- Advancing next-generation IC7Fc molecules into Phase 1 clinical trials for metabolic diseases.
- Testing IC7Fc as an adjunct therapy with GLP-1RAs in preclinical models.
- Understanding the molecular mechanisms by which IC7Fc preserves muscle mass.
- Exploring additional therapeutic applications for this innovative approach.
This research represents a potential breakthrough in treating metabolic diseases whilst avoiding the muscle loss that compromises current weight-loss therapies.